Lipostar
Want to download, evaluate or know more about Lipostar?
Please refer to Mass
Analytica

Lipostar 2 is a comprehensive, vendor-neutral software for LC-MS/MS-based lipidomics (DDA and DIA), which includes a large number of features including: raw data import and peak detection, identification, quantification, statistical analysis, trend analysis and biopathways analysis.
Lipostar 2 finds application in untargeted and semi-targeted lipidomics, including stable isotope labelling experiments. Within a Lipostar session, different modes of lipidomics analysis can be combined to increase knowledge and obtain a more comprehensive analysis of lipid profiles.
Key Features
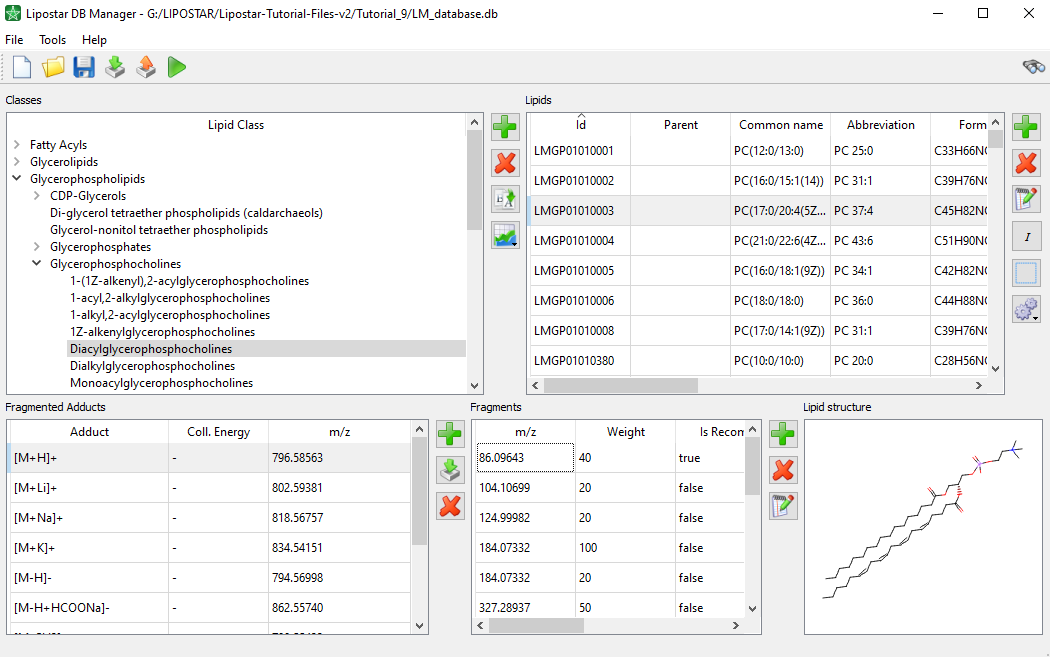
- The DB Manager module that enables the generation of databases of fragmented lipids by applying fragmentation rules provided by the software or by importing experimental MS/MS data
- A flexible lipid identification approach that includes:
- a spectral matching approach
- high-throughput bottom-up approach, based on class-specific fragment recognition
- high-throughput identification of oxidized species.
- A gap-filler algorithm to reduce missing values
- Various plots to visualize and refine identification results
- Various multivariate statistical analysis tools
- Lipid pathways
Enhancements in Lipostar 2
Data Processing
- More instruments supported. Now Lipostar 2 reads the most common file formats:
- Agilent Q-Tof(*.d): AutoMS and full scan at multiple energies of collision (All Ions).
- Waters (*.raw): MSe, HDMSe, DDA, and MSMS, SONAR
- Thermo-Fisher (*.RAW): Ion-Trap and Orbitrap, Exactive, Q-Exactive, DDA and AIF
- ABSCiex *.wiff file format.
- Bruker (*.d): QTof, FT-ICR, TIMS-TOF data dependent scan.
- Shimadzu (*.lcd): QTof
- Data processing can be run in the background.
Data Analysis
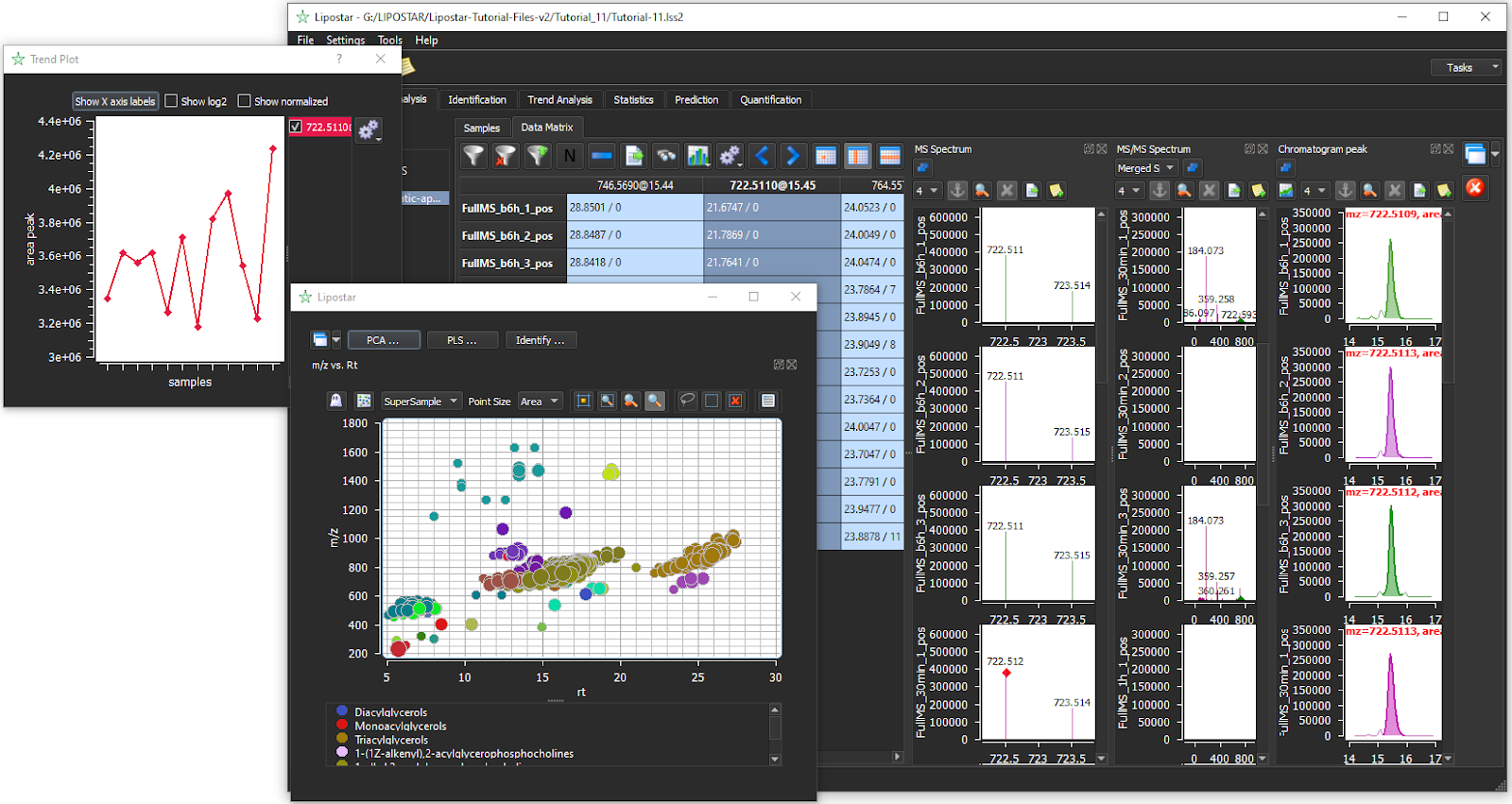
- Trend analysis for global lipid profiling
Identification
- New fragmentation rules for automatic lipid identification
- Lipid database generation from in-house data
- Improved adduct and in source fragmentation clustering
- Customized adducts support
- Transfer of identification results to submatrices
- Kendrick mass defect plot
- Use of Waters CCS values for identification scores
Quantification
- New handling of adduct information
Lipid pathways
- Updated and new biopathways maps available (metabolism & disease)
Cross-talk with other software
- Connection to LipidLynxX for lipid annotation
- connection to LPPTiger for in depth identification of oxidized species
Tutorials
- 14 updated and new tutorials are available
References
-
Goracci L; Tortorella S; Tiberi P; Pellegrino RM; Di Veroli A; Valeri A;
Cruciani G,
Lipostar, a Comprehensive Platform-Neutral Cheminformatics Tool for Lipidomics.
Anal. Chem., 2017, 89 (11), pp 6257–6264 - Capece D, D'Andrea D, Begalli F, Goracci L, et al.
Enhanced triacylglycerol catabolism by Carboxylesterase 1 promotes aggressive colorectal carcinoma.
J Clin Invest. 2021;131(11):e137845 - Terao M, Goracci L, Celestini V, Kurosaki M, et al.
Role of mitochondria and cardiolipins in growth inhibition of breast cancer cells by retinoic acid.
J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38, 436 (2019). Erratum in: J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Dec 18;38(1):496. PMID: 31665044; PMCID: PMC6821005. - Goracci L, Valeri A, Sciabola S, Aleo MD, et al.
A Novel Lipidomics-Based Approach to Evaluating the Risk of Clinical Hepatotoxicity Potential of Drugs in 3D Human Microtissues.
Chem Res Toxicoly 2020 Jan 21;33(1):258-270. Epub 2019 Dec 24. PMID: 31820940. -
Ni Z, Goracci L, Cruciani G, Fedorova M.
Computational solutions in redox lipidomics - Current strategies and future perspectives.
Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 Nov 20;144:110-123. Epub 2019 Apr 26. PMID: 31035005. -
La Barbera G, Antonelli M, Cavaliere C, Cruciani G, et al.
Delving into the Polar Lipidome by Optimized Chromatographic Separation, High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry, and Comprehensive Identification with Lipostar: Microalgae as Case Study.
Anal Chem. 2018 Oct 16;90(20):12230-12238. Epub 2018 Sep 24. PMID: 30204416. -
Torquato P, Giusepponi D, Alisi A, Galarini R, et al.
Nutritional and lipidomics biomarkers of docosahexaenoic acid-based multivitamin therapy in pediatric NASH.
Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 14;9(1):2045. PMID: 30765737; PMCID: PMC6375912. - Camera E, Ludovici M, Tortorella S, Sinagra JL et al.
Use of lipidomics to investigate sebum dysfunction in juvenile acne.
J Lipid Res. 2016 Jun;57(6):1051-8. Epub 2016 Apr 27. PMID: 27127078; PMCID: PMC4878189.
